
What is the most valuable asset one can gain from a person? Before I became an artificial intelligence researcher, I worked as a part-timer in many fields. One of the most memorable part-time jobs I worked at was playing a role of movie extra. I had the opportunity to participate in the film ‘The Scam’ (2009), and took on the roles of a passenger, a man smoking in front of a building, and a student studying in a library. At that time, I was aware that my face could be used in a movie, and I was paid a pretty decent salary.
However, what if the image of my face is taken and used unknowingly? In fact, in the world we live in, CCTV cameras are installed everywhere for the purpose of safety.
According to the current state of CCTV installation and operation in Korea [i], the number of CCTV cameras has steadily increased, and the number of CCTVs installed by public institutions alone is over 1 million. In addition, if non-public cameras such as vehicle black boxes and commercial security cameras are included, there are no more blind spots across the nation. Most of the collected images are automatically discarded within 30 days, unless there are special circumstances. From the point of view of protecting personal portrait rights, it seems very reasonable.
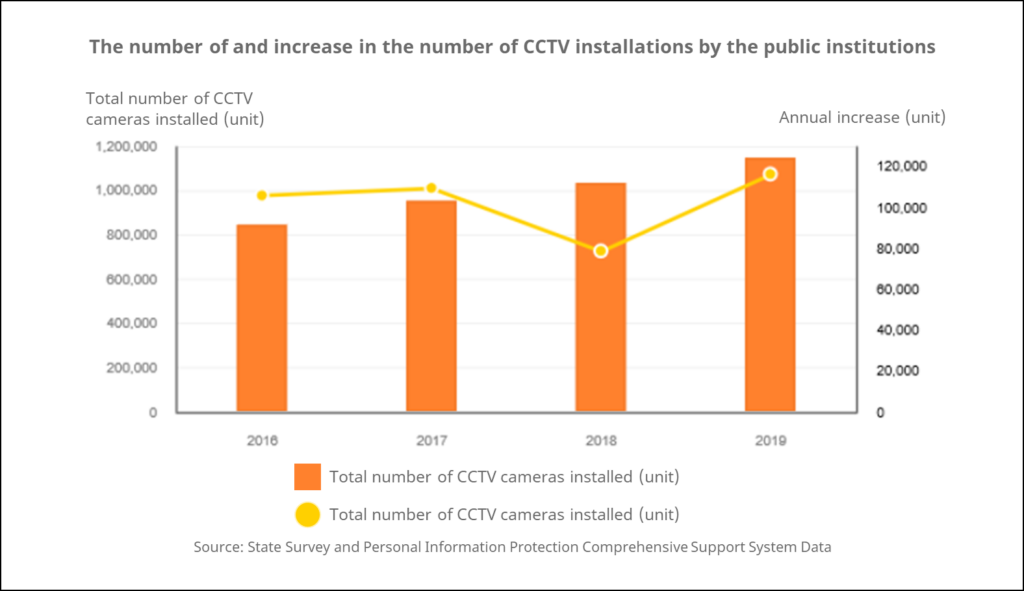
On the other hand, industry-university-research institutes led by AI technology have a different opinion. It is disappointing to see the vast amount of data that can be used for artificial intelligence simply be discarded. Park Yong-man, chairman of the Korea Chamber of Commerce and Industry, held a press conference at the Korea Chamber of Commerce and Industry in November 2019, saying “The data industry is said to be the crude oil of the future, but now the situation is such that the oil extraction itself is blocked. The future of the industrial revolution or even the future of the industry seems to be shrouded in doubt.” In the same month, Kakao co-CEO Yeo Min-soo also said at a meeting, “If there is a company that intentionally leaks data, they can be fined more than their operating profit.” [ii]
On January 9, 2020, three acts related to data were passed. It became possible to use ” pseudonym information” that blocked concerns over data transactions and personal information leakage, which are key resources in the era of the 4th industrial revolution. Alias information refers to information that makes it impossible to recognize a specific individual by de-identifying sensitive information such as name and resident registration number.[iii] Since the scope of analysis and utilization of collected data is expanding, pseudonym information is expected to be used without the consent of the subject in question when used for statistical and scientific research, and public interest records. Accordingly, methods for pseudonymizing personal identification information of vast amounts of data collected at home and abroad are being under active study.

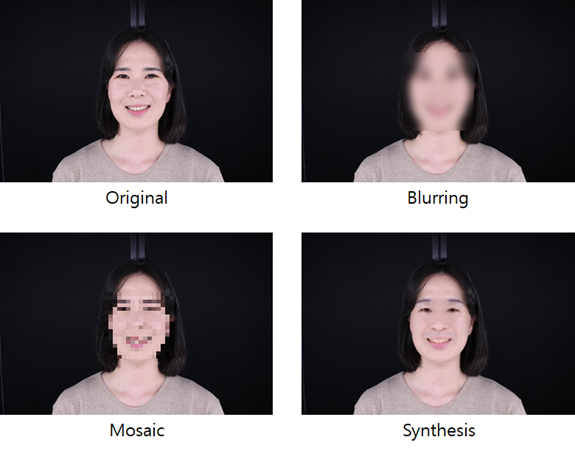
Tao Li presented an unidentified processing method, AnonymousNet[iv], at the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR), one of the best academic conferences in computer vision deep learning. In addition to the existing Blurring (blurring) and Pixelation (mosaic), he synthesized realistic alternatives to de-identify the image and proposed a measurable method of privacy. AnonymousNet is designed to be selectively transformable for facial feature attributes and measures whether each attribute is properly de-identified. Facial characteristics attributes are designed to be transformable not only for actual facial characteristics such as age, gender, skin color, hair type, facial expression, and beard, but also for accessories such as glasses and earrings.

Facebook AI Research has published Live Face De-Identification in Video[v], a non-identification processing study applied to video images, by the International Society for Computer Vision (ICCV), one of the best academic conferences in computer science. It is designed to minimize performance degradation in various poses, expressions, illumination conditions, and occlusions. High Level features (eyes, nose, mouth, eyebrows) are changed, and pose, expression, lip shape, lighting, and skin tone are preserved. Facebook AI Research also studied non-identification processing algorithms that compensate for flickering, visual artifacts, and distortion in successive frames.

Original image (top), after de-identification processing (bottom)
Testworks is performing the task of de-identifying personal information in the collected videos. It provides a non-identification processing service for not only an individual’s face but also a vehicle’s license plate. In addition to providing a service to remove personal information through Blur and mosaic, a method of de-identifying the face by converting it into a virtual person, is also in progress. [vi]

In order to use data without problems in artificial intelligence learning and R&D research such as emotion recognition and abnormal behavior detection, Testworks is researching ways to de-identify only personal identification information while maintaining posture, expression, and expression information of characters in the original image. Testworks will also provide a de-identification processing service that can be selected according to the purpose of use in addition to the basic method of de-identification of vehicle license plates.

In my previous contribution, “The Importance of GAN in Creating AI Training Datasets” I mentioned that de-identification processing plays a role as a “waterway” for the data dam business. In addition to the face and vehicle license plates, de-identification studies will be necessary for a variety of information including personal information such as iris, fingerprint, gait, voice, address, name, and resident registration number to facilitate the flow of the dam. I hope that the data ecosystem becomes much more active so that companies that use AI and data can quench their thirst for data and secure global competitiveness.
[i] Public institution CCTVs status, https://www.index.go.kr/potal/main/EachDtlPageDetail.do?idx_cd=2855
[ii] Use of ‘information under false name’ is used without my consent. What is the meaning of the passage of 3 acts related to data?, https://news.mt.co.kr/mtview.php?no=2020010921561656429
[iii] Guidelines for non-identification of personal information, Refer to the Korea Internet & Security Agency (KISA)
[iv] Li, Tao, and Lei Lin. “Anonymousnet: Natural face de-identification with measurable privacy.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. 2019.
[v] Gafni, Oran, Lior Wolf, and Yaniv Taigman. “Live face de-identification in video.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019.
[vi] AI Hub Korean face image AI data, https://aihub.or.kr/aidata/73
※ Testworks’ research utilizing Korean face image AI data disclosed on AI Hub.
[vii] Use of figures from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport https://www.molit.go.kr/carplate/main.jsp

Hyeongbok Kim
Senior researcher, AI R&D Team
Entered Harbin Institute of Technology, Computer Science and Technology, PhD Course with the highest performance as a student under scholarship of the Chinese government
He has returned to Korea due to COVID-19 while working on AI. Currently he is working at AI R&D Team of Testworks. He is interested in social contribution through technology.